代码随想录算法训练营第16天
今日任务
● 104.二叉树的最大深度 559.n叉树的最大深度 ● 111.二叉树的最小深度 ● 222.完全二叉树的节点个数
链接:https://docs.qq.com/doc/DUHBQRm1aSWR4T2NK (opens in a new tab)
104.二叉树的最大深度
自己想法
可以用递归,也可以用迭代,迭代的话就是(昨天练习的)层序遍历,每遍历一层,深度加一。
递归方法中,本题可以使用前序(中左右),也可以使用后序遍历(左右中),使用前序求的就是深度,使用后序求的是高度。
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
下面代码为:递归(后序)
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
int depth = 0;
depth = invert(root);
return depth;
}
// 1.返回值:当前节点(下面的)高度
int invert(TreeNode node) {
// 2.结束条件
if(node == null) return 0;
// 3.递归逻辑
int left_depth = invert(node.left) + 1;
int right_depth = invert(node.right) + 1;
return Math.max(left_depth, right_depth);
}
}n叉树的最大深度
自己想法
递归法
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
int depth = 0;
depth = invert(root);
return depth;
}
// 1.返回值:当前节点下面的深度
int invert(Node node) {
// 2.结束条件
if(node == null) return 0;
// 3.递归逻辑
int depth = 1;
for (Node child : node.children){
depth = Math.max(depth, invert(child) + 1);
}
return depth;
}
}111.二叉树的最小深度
自己想法
下面代码为:递归(前序)
class Solution {
public int min_depth;
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
this.min_depth = -1;
if(root == null) return 0;
invert(root, 0);
return this.min_depth;
}
// 1.返回值:空,因为用this.min_depth来记录了
void invert(TreeNode node, int now_depth) {
// 2.返回条件
if(node == null) return;
// 3.递归逻辑
now_depth++;
// 3.1.如果是叶子节点,那么和this.min_depth比较
if(node.left == null && node.right == null) {
if(this.min_depth == -1) this.min_depth = now_depth;
else this.min_depth = Math.min(this.min_depth, now_depth);
}
// 3.2.如果不是叶子,那么走左右
invert(node.left, now_depth);
invert(node.right, now_depth);
}
}回顾
-
求高度,用后序遍历,递归返回的就是高度
-
求深度,用前序遍历,递归不返回,用参数来记录深度。如果需要找最小深度,那么需要用全局变量来记录最小深度
222.完全二叉树的节点个数
自己想法
直接递归,不仅适用于完全二叉树,也适用于普通二叉树。
-
时间复杂度:O(n)
-
空间复杂度:O(log n),算上了递归系统栈占用的空间
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
return invert(root);
}
// 1.返回值:当前node下的节点数(包括自己)
int invert(TreeNode node) {
// 2.结束条件
if(node == null) return 0;
// 3.递归逻辑:当前node下的节点数等于左+右+1(自己)
int left_nodes = invert(node.left);
int right_nodes = invert(node.right);
return left_nodes + right_nodes + 1;
}
}题解想法
利用完全二叉树的性质:满二叉树(特殊的完全二叉树)的结点数为:2^depth - 1
完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:就是满二叉树,情况二:最后一层叶子节点没有满。
-
对于情况一,可以直接用 2^树深度 - 1 来计算,注意这里根节点深度为1。
-
对于情况二,分别递归左孩子,和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树,然后依然可以按照情况1来计算。
如何去判断一个左子树或者右子树是不是满二叉树呢?
在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右遍历的深度,那说明就是满二叉树
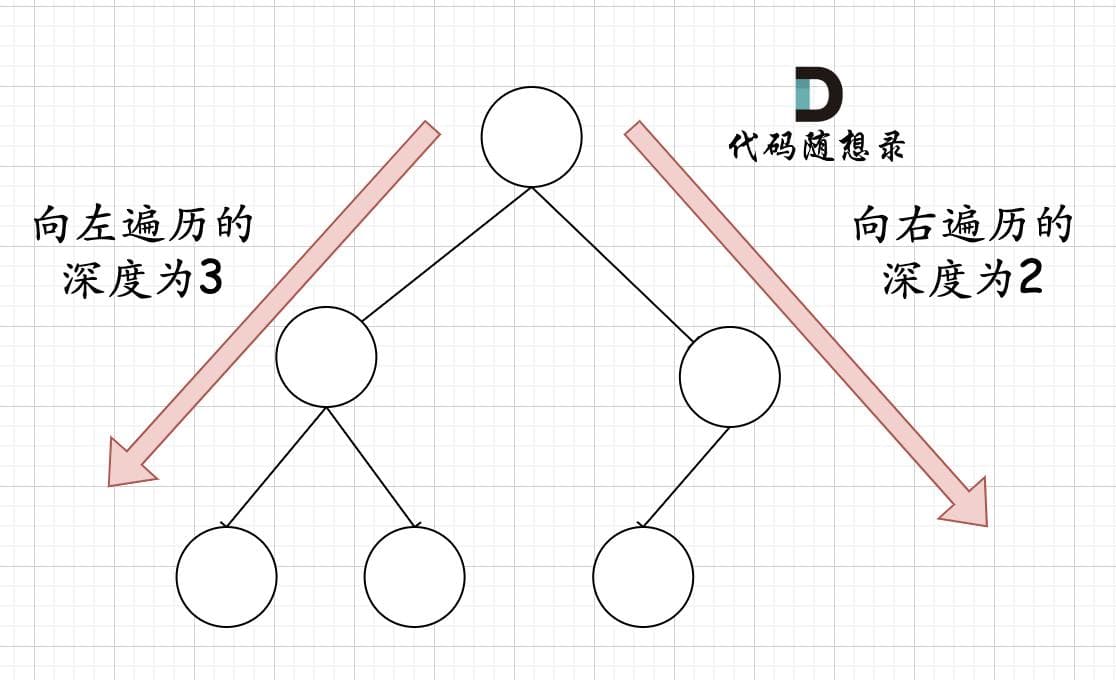
-
时间复杂度:O(log n x log n)
-
空间复杂度:O(log n)
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
return invert(root);
}
// 1.返回值:当前node下的节点数(包括自己)
int invert(TreeNode node) {
// 2.结束条件
if(node == null) return 0;
// 3.递归逻辑:当前node下的节点数等于左+右+1(自己)
// 3.1.判断左右分别是不是完全二叉树
TreeNode left = node.left;
TreeNode right = node.right;
int left_depth = 0, right_depth = 0;
while(left != null) {
left = left.left;
left_depth++;
}
while(right != null) {
right = right.right;
right_depth++;
}
// 3.2.是的话用公式计算
if(left_depth == right_depth)
return (2 << left_depth) - 1; // 移位操作计算 2^left_depth-1
// 3.3.不是的话继续递归
return invert(node.left) + invert(node.right) + 1;
}
}